Resource Details
Resource Format
Categories
Share:
When a clinician makes a formal diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder, they use the criteria laid out in the Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Volume V, 2013.
It reads as follows:
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Diagnostic Criteria 299.00 (F84.0)
Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive; see text):
Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication; to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures; to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships, ranging, for example, from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts; to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or making friends; to absence of interest in peers.
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior (see Table below).
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive; see text):
Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech (e.g., simple motor stereotypies, lining up toys or flipping objects, echolalia, idiosyncratic phrases).
Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior (e.g., extreme distress at small changes, difficulties with transitions, rigid thinking patterns, greeting rituals, need to take same route or eat same food every day).
Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus (e.g., strong attachment to or preoccupation with unusual objects, excessively circumscribed or perseverative interests).
Hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input or unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment (e.g., apparent indifference to pain/temperature, adverse response to specific sounds or textures, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement).
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior (see Table below).
Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life).
Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning.
These disturbances are not better explained by intellectual disability (intellectual developmental disorder) or global developmental delay. Intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder frequently co-occur; to make comorbid diagnoses of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability, social communication should be below that expected for general developmental level.
Note: Individuals with a well-established DSM-IV diagnosis of autistic disorder, Asperger’s disorder, or pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified should be given the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. Individuals who have marked deficits in social communication, but whose symptoms do not otherwise meet criteria for autism spectrum disorder, should be evaluated for social (pragmatic) communication disorder.
Specify if: With or without accompanying intellectual impairment
With or without accompanying language impairment
Associated with a known medical or genetic condition or environmental factor (Coding note: Use additional code[s] to identify the associated medical or genetic condition.)
Associated with another neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder (Coding note: Use additional code[s] to identify the associated neurodevelopmental, mental, or behavioral disorder[s].)
With catatonia (refer to the criteria for catatonia associated with another mental disorder, pp. 119-120, for definition) (Coding note: Use additional code 293.89 [F06.1] catatonia associated with autism spectrum disorder to indicate the presence of co-morbid catatonia.)
Social (Pragmatic) Communication Disorder
Diagnostic Criteria 315.39 (F80-.89)
Persistent difficulties in the social use of verbal and nonverbal communication as manifested by all of the following:
Deficits in using communication for social purposes, such as greeting and sharing information, in a manger that is appropriate for the social context.
Impairment of the ability to change communication to match context or the needs of the listener, such as speaking differently in a classroom than on a playground, talking differently to a child than to an adult, and avoiding use of overly formal language.
Difficulties following rules for conversation and storytelling, such as taking turns in conversation, rephrasing when misunderstood, and knowing how to use verbal and nonverbal signals to regulate interaction.
Difficulties understanding what is not explicitly stated (e.g., making inferences) and nonliteral or ambiguous meanings of language (e.g., idioms, humor, metaphors, multiple meanings that depend on the context for interpretation).
The deficits result in functional limitations in effective communication, social participation, social relationships, academic achievement, or occupational performance, individually or in combination.
The onset of the symptoms is in the early developmental period (but deficits may not become fully manifest until social communication demands exceed limited capacities).
The symptoms are not attributable to another medical or neurological condition or to low abilities in the domains of word structure and grammar, and not better explained by autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability (intellectual developmental disorder), global development delay, or another mental disorder.
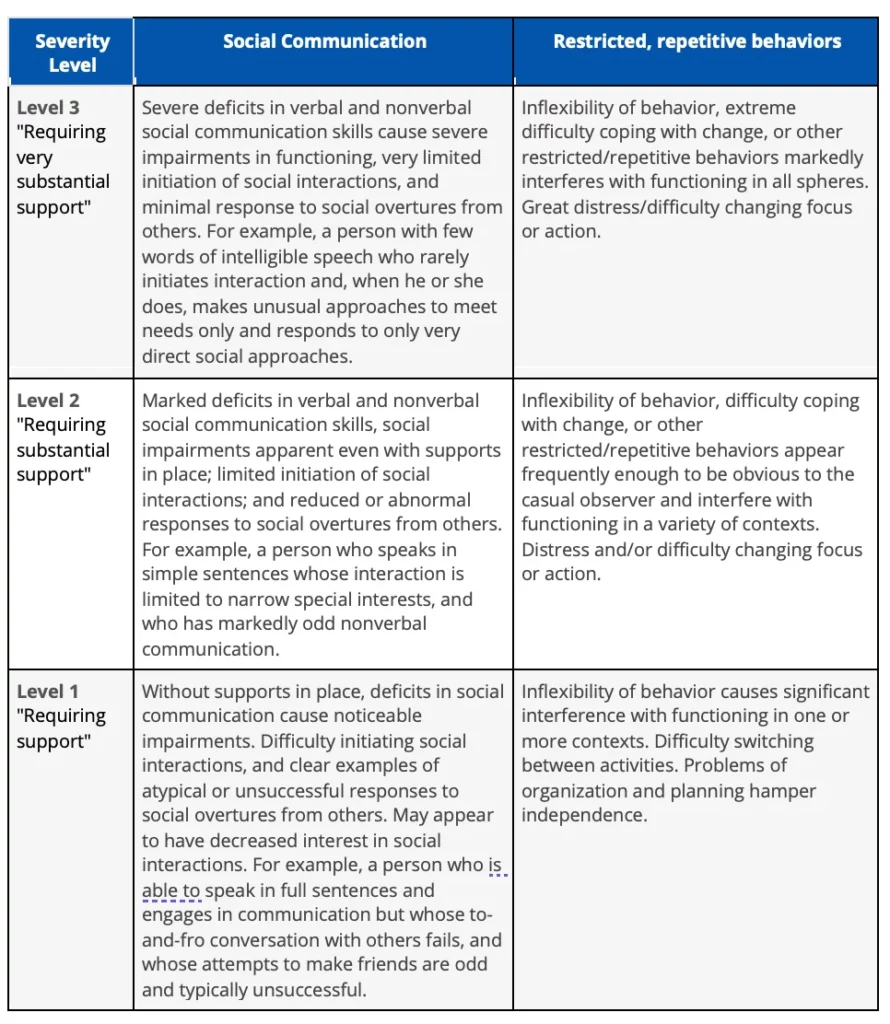
Reprinted with permission from American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Copyright © 2013. American Psychiatric Association. All Rights Reserved. Permission from the APA is required to reproduce DSM-5 Criteria and any Related Tables.
More information from AAHR

More Resources
Learn more about common medical conditions and ways of understanding and supporting adults with autism throughout the lifespan.





